3D Printing vs. Laser Cutting: What’s the Difference?
If a student or colleague asked you what the difference between a 3D printer and a laser cutter was, what would you say? Is this the type of question you can answer confidently with your head held high, or the type that would have you faking an injury to avoid answering… our students aren’t the only ones who do this, right? As educators, it’s important that we continuously keep up with the latest technological innovations to ensure that we can give our students the proper tools and training to succeed in the real world. The problem is, when you’re outside of the Maker world, resources used to explain these technologies are often technical, daunting, and inaccessible to those in the field of education.
Core Differences
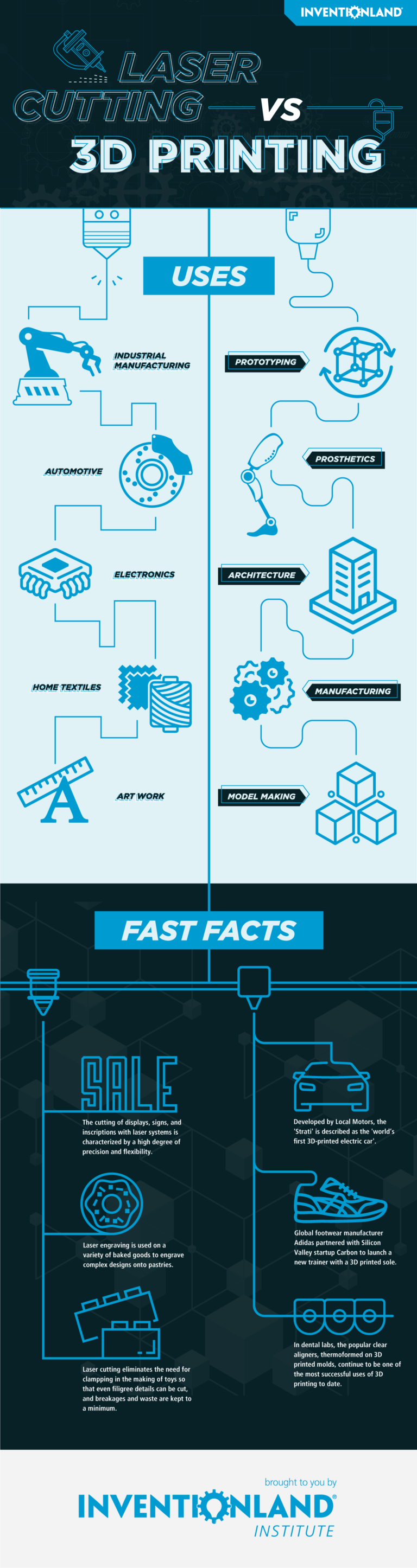
To start off, let’s dive into the very simple difference between the two machines. Laser cutting is a subtractive manufacturing process, meaning that it precisely cuts away material from the source to create the desired shape. On the complete opposite end of the spectrum, there’s 3D printing, which is an additive manufacturing process meaning that the machine is adding material layer by layer to create a 3D version of a design. So, keeping it as bare-bones as possible, laser cutting is taking material away while 3D printing is adding/creating material.
What Can You Do With a 3D Printer?
3D Printing involves creating a file using 3D modeling software and choosing the material you want to build out of. You can 3D print plastics, resin parts, and you can even 3D print metals as well. The important thing to keep in mind is adapting the material you choose to the particular project on which you’re working. And, when you’re in the prototyping stage, making sure to start with less durable and expensive materials as you tweak your design.
As 3D Printing technology continues to develop, the project possibilities grow exponentially. As one example, 3D printing has now been used to completely construct houses from the ground up in under 24 hours. It is used in the architectural industry through the many steps of construction, starting with modeling. Using affordable materials to create 3D models of their designs not only allows architects to have a piece to show customers, but seeing if the design works in real life will allow them to make any necessary adjustments to the 3D file.
This form of printing also allows you to print large parts made of durable materials, which is used for the construction of houses. Using a giant robotic arm that looks like something out of a sci-fi thriller, large-scale 3D printers are able to use materials like concrete to 3D print a house entirely as one part. Using this process to construct homes allows a reduction in cost and material waste. In addition, since a machine can work continuously, it allows us to create homes quicker and with more accuracy.
Outside of architecture, 3D printing has many additional and equally useful purposes. It can be used for anything from jaw reconstruction to prosthetic limbs to fashion accessories to robotics. In recent years, 3D printers have even been used to create intricately crafted foods like cakes, cookies, pasta, chocolate, etc. And, as this technology advances, we’ll likely see many more equally innovative creations over the course of our lifetimes.
What Can You Do With a Laser Cutter?
A laser cutter is capable of two separate techniques- laser cutting and laser engraving. Laser cutting utilizes a high-powered laser to cut the material into various shapes whereas a laser engraver can engrave a piece with a design. You can laser cut a variety of materials such as acrylic, MDF, plywood, cardboard, & POM. Generally, laser cutters are more intuitive and easier to use than 3D printers because they’re a contained system. Just the concept of cutting a flat piece into segments or into a design is easier to program and construct than building a three-dimensional object from the ground up.
Essentially, laser cutting can be used to cut out and create intricate designs with a perfection that is impossible to create with free-hand cutting. Due to the intuitive nature of the machine, people have used laser cutting for a variety of projects from creating artistic clocks, to attaching logos to travel mugs, to even putting engravings onto food like pies.
Which Should You Use?
In our experience, we’ve seen people use these two terms fairly interchangeably- even giving us some fun variations we’ve never heard of like ‘3D laser cutting’ (which, interesting as it sounds, is not a thing). But, walking through the processes of these two machines, one can see that they’re truly the complete antithesis of each other. The additive manufacturing process used in 3D printing allows you to create everything from high-quality prototypes to even your final product. It can help you cut down on material waste/cost for your project and 3D modeling software allows you to create complex three-dimensional designs.
Subtractive manufacturing such as laser cutting allows you to carve out a design as opposed to constructing one. This machine allows you to work on a flat surface, but will only allow you to create flat parts. So, if you need a design to be three-dimensional, you’d need to cut out multiple parts and mold them together if you’re going with laser cutting for your project. Since you’re working on a flat surface, you can create extremely intricate designs with a high rate of precision. It also may end up being less expensive to laser cut pieces as opposed to 3D printing if you’re working on creating a larger object.
Ultimately, though, they both work extremely well together. And, because they’re both crucial processes in today’s manufacturing world, they’re equally important for our students to learn.
Want to give your classroom the tools it needs to easily teach 3D printing/laser cutting in both a practical and ideological way? Check out our Maker Kits and Maker Charts!